Knee pain is a common complaint that can hinder everyday activities from walking and working to exercising and enjoying leisure time. Whether caused by injury, overuse, or degenerative conditions like arthritis, discomfort in the knee can make even simple tasks feel like a challenge. Fortunately, a wide range of techniques and home remedies can offer relief, improve mobility, and help maintain a healthy lifestyle.
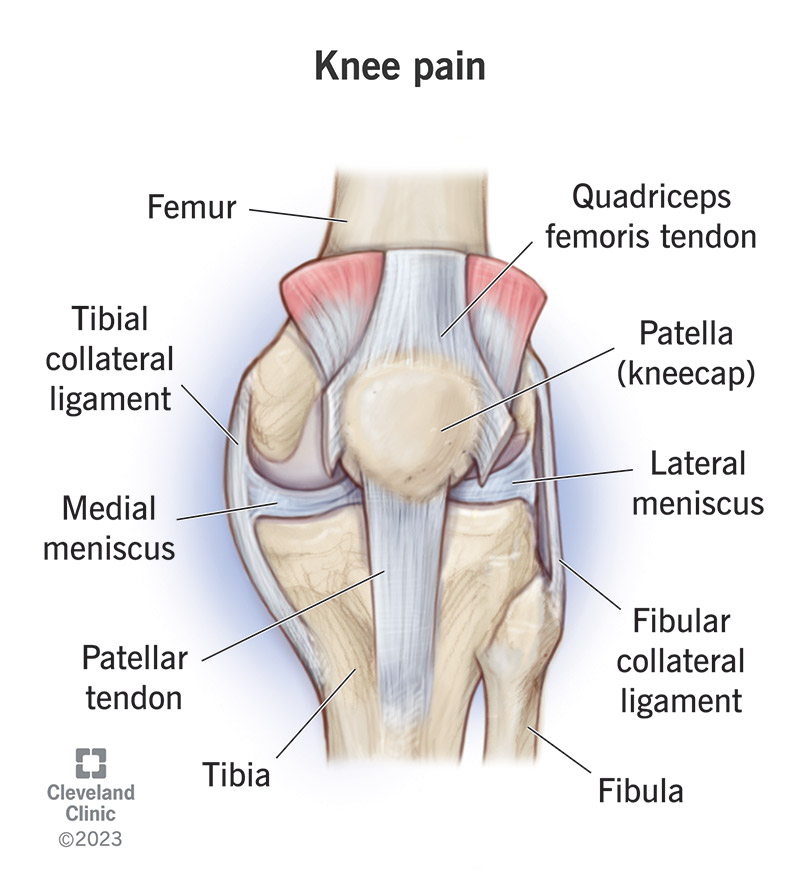
The knee is a complex hinge joint that supports the majority of the body’s weight while allowing a wide range of motion. It comprises bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that work together to enable activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs. Common causes of knee pain include traumatic injuries (such as ligament tears or fractures), overuse from repetitive movements, and chronic conditions like osteoarthritis. Penn and Better Health describe how misalignment, wear and tear, or even muscle imbalances in the hips or ankles can contribute to knee discomfort. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for choosing the most appropriate treatment and prevention strategy.
Immediate Home Remedies for Knee Pain Relief
Before seeking professional treatment, many people find that several self-care techniques can provide immediate relief from knee pain. Here are some well-established methods:
The RICE Method
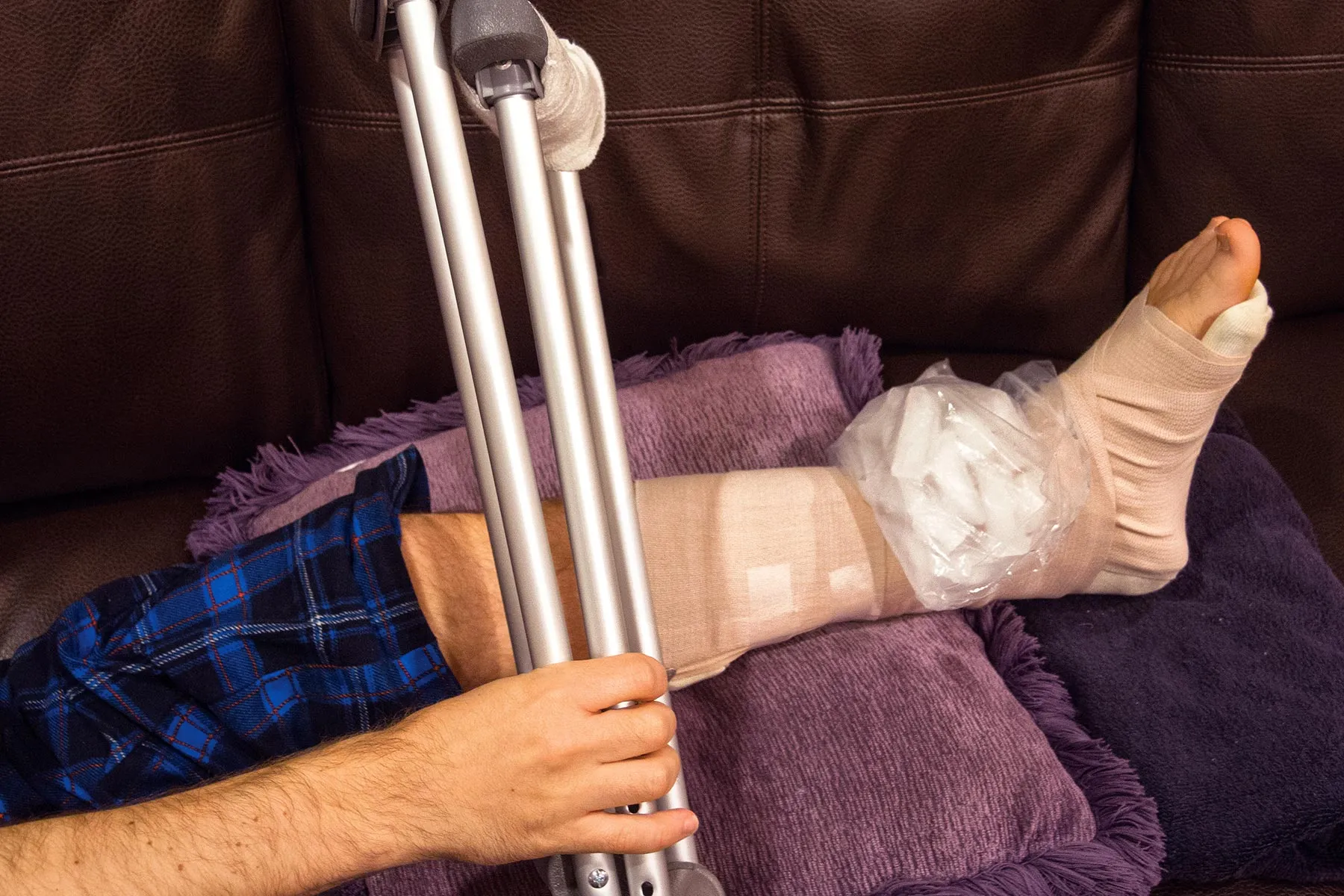
A time-tested approach is the RICE method, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. As explained by WebMD, this method helps reduce swelling and pain after a minor injury.
- Rest: Give the knee a break to avoid further stress on the joint.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack for 15–20 minutes every few hours to reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Compression: Use a bandage or brace to provide support and help control swelling.
- Elevation: Prop up the knee on pillows to improve blood flow and decrease swelling.
Over-the-Counter Medications and Topical Treatments
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. For those who prefer a more localized treatment, topical gels like Voltaren offer targeted relief without the systemic effects of oral medications. These topical treatments penetrate the skin to ease discomfort and are particularly useful when used in combination with other self-care techniques.
Weight Management and Lifestyle Adjustments
Excess weight can place additional strain on the knees, exacerbating pain and accelerating joint degeneration. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise not only reduces knee stress but also promotes overall well-being. Medical News Today highlights that even modest weight loss can significantly lessen the pressure on knee joints.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
While rest is important after an injury, remaining active is key to long-term knee health. Incorporating specific exercises can strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Stretching Exercises
Regular stretching can improve range of motion and relieve tension in the muscles around the knee. For instance, gentle stretches targeting the calves, quadriceps, and hamstrings can ease tightness that might be pulling on the knee joint. Healthline suggests starting with simple stretches such as:
- Calf Stretch: Stand facing a wall, step one leg back, and press your heel into the floor until you feel a stretch in the calf.
- Quadriceps Stretch: While standing, grasp your ankle and gently pull your heel toward your buttock to stretch the front of your thigh.
- Hamstring Stretch: Sit on the floor with one leg extended and gently lean forward from the hips, reaching for your toes.
These stretches not only improve flexibility but also help in maintaining proper knee alignment during movement.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the knee is crucial for stability and reducing pain. Several low-impact exercises can build muscle strength without putting excessive strain on the joint:
- Side-Leg Raises: Lying on one side, lift the top leg upward slowly and lower it back down. This exercise targets the outer thigh muscles and hip abductors.
- Straight Leg Raises: Lying on your back, keep one leg straight while lifting it to the height of the opposite bent knee. This move helps strengthen the quadriceps without stressing the knee joint.
- Half Squats: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart and perform partial squats. This exercise works the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps while keeping the pressure on the knee within a manageable range.
- Calf Raises: Stand near a wall or chair for balance and slowly rise up on your toes, then lower back down. This strengthens the calf muscles and improves overall lower leg stability.
According to Houston Methodist, integrating these exercises gradually into your routine can help reduce pain and prevent further injury. It is important to focus on proper form and start with a low number of repetitions, gradually increasing as strength improves.
Low-Impact Activities
For those with persistent knee pain, switching to low-impact activities can be beneficial. Swimming, cycling, and aqua-walking are excellent alternatives to high-impact sports. These activities minimize joint stress while still providing cardiovascular benefits and muscle strengthening. Versus Arthritis emphasizes that staying active with low-impact exercises can prevent muscle weakness and maintain joint mobility without aggravating pain.
Alternative Therapies and Advanced Treatments
In addition to home remedies and exercise, several alternative therapies and medical treatments may offer relief for chronic knee pain.
Massage and Myofascial Release
Massage therapy and techniques like foam rolling can relieve muscle tightness and improve blood flow to the knee area. These methods work by easing tension in the muscles and connective tissue that support the joint. While evidence on the long-term benefits is still emerging, many find that a good massage helps reduce discomfort and increases mobility.
Acupuncture and Essential Oils
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting fine needles at specific points on the body to stimulate healing and reduce pain. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may offer temporary relief for knee pain associated with osteoarthritis. Similarly, essential oil aromatherapy is reported by some to ease symptoms, although research on its efficacy remains inconclusive. Medical News Today discusses how these alternative therapies might complement conventional treatments.
Injections and Regenerative Medicine
For more severe or persistent knee pain, medical interventions such as corticosteroid injections or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy may be considered. Cortisone injections can provide significant temporary relief by reducing inflammation, while PRP injections aim to harness the body’s natural healing processes by using concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood. Mass General notes that these treatments are typically reserved for cases where other conservative measures have failed, and they may be part of a broader rehabilitation program.
Physical Therapy
Professional physical therapy is often recommended for individuals who experience ongoing knee pain. A physical therapist can tailor an exercise program to address specific weaknesses or imbalances, help improve joint stability, and educate on proper movement techniques. The Mayo Clinic advises that guided physical therapy can not only alleviate pain but also help prevent future injuries by ensuring the correct form during exercise.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Preventing knee pain is as important as treating it. Small lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference over time.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying extra pounds puts additional strain on the knee joints. A balanced diet coupled with regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, thereby reducing the load on your knees. Even a slight weight reduction can ease symptoms of knee pain and slow the progression of conditions like osteoarthritis. Medical News Today emphasizes that healthy eating and weight management are key components in the long-term care of knee health.
Use Proper Footwear and Supports
Supportive footwear can play a vital role in reducing knee pain. Shoes with good arch support and cushioning help absorb shock and minimize the impact on your knees during walking or running. In some cases, orthotic inserts or knee braces may be recommended by healthcare providers to improve alignment and reduce stress on the joint. Penn highlights that the right footwear is a simple yet effective measure to prevent knee discomfort.
Adjusting Daily Habits
Simple changes in daily activities can also help manage knee pain. Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing in one position; instead, take breaks to stretch and move around. When climbing stairs, try to lead with the leg that experiences less pain, and always use handrails for added support. Additionally, incorporating regular low-impact exercises can keep the muscles around the knee strong and flexible, reducing the likelihood of injury.
Ergonomic Adjustments
For those who work at a desk, setting up an ergonomic workstation can minimize the strain on the knees. Adjusting your chair, desk height, and computer setup so that you are not forced to maintain awkward positions can help prevent chronic pain. Regular movement and stretching breaks are highly recommended to keep the muscles active and relieve tension.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many techniques can alleviate mild to moderate knee pain, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention.
If knee pain is accompanied by severe swelling, inability to bear weight, or persistent discomfort that does not improve with home treatments, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
NHS advises that if pain lasts for several weeks or if the knee locks, clicks, or shows signs of infection (such as redness, heat, or fever), a doctor’s evaluation is necessary.
Moreover, if an injury has caused a sudden “pop” in the knee or if the pain intensifies during movement, these could be indicators of a ligament tear or other structural damage. In such cases, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs—often recommended by Mayo—can help determine the extent of the injury and guide appropriate treatment, which may include physical therapy or, in rare cases, surgical intervention.
Advanced Therapies and Future Directions
For individuals with chronic knee pain that does not respond to traditional treatments, advanced therapies are emerging as promising alternatives.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative treatments such as PRP injections and stem cell therapy are gaining attention for their potential to improve joint function and reduce pain. These therapies work by stimulating the body’s natural repair mechanisms, using concentrated growth factors from the patient’s own blood to promote healing. Northwestern is exploring how these innovative approaches might revolutionize knee pain management in the near future.
Customized Orthotics and Bracing
The development of customized knee braces and orthotic devices can provide tailored support to individuals suffering from knee pain. These devices help correct misalignments, distribute weight evenly, and reduce undue stress on the joint. Advances in technology now allow for more personalized options, which can be especially beneficial for athletes or those with specific biomechanical issues.
Integrative Pain Management
An integrative approach to knee pain often involves combining physical therapy, alternative treatments, and medical interventions. This holistic strategy ensures that all aspects of pain management are addressed, from inflammation and muscle tension to long-term joint stability. Patients are encouraged to work with healthcare providers who understand the value of combining different modalities to create a comprehensive treatment plan.
Bringing It All Together
Managing knee pain is a multifaceted challenge that requires a balanced approach. Whether it is through simple home remedies like the RICE method, targeted exercises to build muscle strength and flexibility, or more advanced treatments when necessary, the key is consistency and awareness. By understanding the underlying causes and addressing each aspect of knee health, it is possible to reduce pain, improve mobility, and ultimately enjoy a more active lifestyle.
Maintaining regular exercise routines, adjusting daily habits, and taking preventive measures—such as proper weight management and using supportive footwear—can have a profound impact on knee health over time. It is important to remember that each individual’s experience with knee pain is unique. Techniques that work well for one person may need to be tailored for another, emphasizing the need for personalized care.
Sources: