Joint pain can feel like an uninvited companion that hinders daily activities and diminishes quality of life. Whether the discomfort stems from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or an injury, finding effective relief is crucial. Over the years, a variety of treatments have emerged from traditional over-the-counter medications and physical therapies to innovative alternative approaches. This article provides an in-depth look at the top joint pain relievers available today, explains how they work, and reviews their effectiveness, all while breaking down complex concepts into simple, relatable terms.

Before delving into treatments, it is important to understand what causes joint pain. The joints are complex structures where bones meet, cushioned by cartilage and supported by tendons and ligaments. Over time or after an injury, these components may deteriorate or become inflamed. For example, osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage gradually wears down, leading to pain and stiffness. On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining, causing chronic inflammation.
Joint pain can manifest in various ways sharp or dull, constant or intermittent—and may affect one joint or several at once. Factors such as aging, repetitive strain, and even genetic predisposition play a role. With a clearer understanding of joint pain’s nature, the focus can shift to exploring the array of treatments designed to alleviate it.
Categories of Joint Pain Relievers
Pharmacologic Options
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are often the first line of defense against joint pain. These include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and meloxicam reduce inflammation and relieve pain. They are effective for many individuals dealing with mild to moderate joint discomfort. In fact, studies show that NSAIDs can significantly ease joint pain and improve function in conditions like arthritis. For more details on common pain medications and their usage, see this overview of common pain medications.
- Acetaminophen: This drug works by altering the way the brain perceives pain, though it does not address inflammation. It is particularly useful for those who cannot tolerate NSAIDs.
- Topical treatments: For localized pain, topical gels such as Voltaren gel and topical lidocaine offer relief by delivering active ingredients directly to the painful area. These treatments reduce systemic side effects and are especially popular among individuals with joint pain that is concentrated in a specific spot. Shop here.
While prescription opioids have been used to manage severe pain, they come with significant risks including dependency and various adverse effects. As a result, there has been a marked shift toward safer alternatives. For insights on reducing opioid use and exploring other options, consider this resource on alternatives to opioids.
Non-Surgical and Physical Therapy Approaches
For many, surgery is not the first choice for managing joint pain. Instead, non-surgical treatments can be highly effective:
- Physical Therapy and Exercise: Customized exercise plans can strengthen the muscles around affected joints, thereby reducing stress on the joints themselves. Targeted stretching and low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking not only improve joint stability but also enhance overall mobility. Research shows that regular physical activity is integral to managing chronic joint pain and improving function.
- Chiropractic Care: A holistic approach that involves spinal and joint adjustments, chiropractic care works by addressing misalignments that contribute to joint pain. Many patients have reported long-lasting relief from chiropractic treatments that focus on both pain reduction and overall wellness.
- Foot Orthoses: For pain in specific joints—such as the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint in the foot—customized orthoses can redistribute pressure and improve biomechanics. A case-series study has shown that foot orthoses can significantly reduce pain, even if the expected changes in joint movement are not always apparent.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Beyond conventional medications and physical therapy, alternative treatments are gaining popularity for their natural approach and fewer side effects:
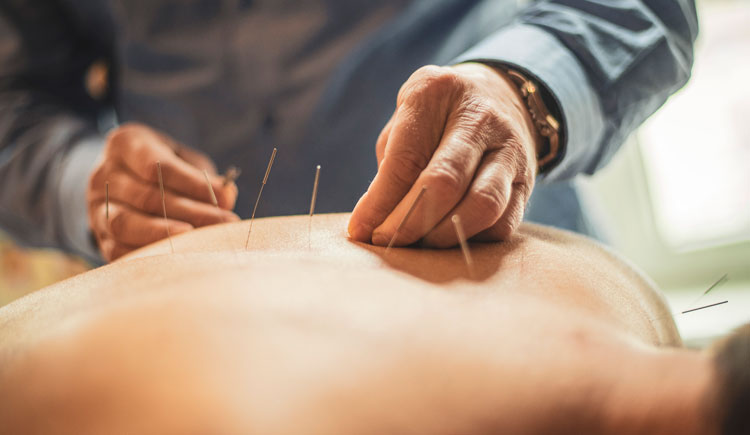
- Acupuncture: This ancient technique has been used for centuries to relieve pain and improve bodily function. Modern research is now uncovering the science behind acupuncture, revealing how it activates specific nerve pathways to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Discover the science of acupuncture and its role in managing chronic joint pain.
- Cupping Therapy: Another traditional method, cupping therapy involves creating suction on the skin to promote blood flow and stimulate healing. Although the scientific community is still exploring its full range of benefits, many patients have reported relief from cupping sessions. For more on how cupping works, see this cupping therapy guide.
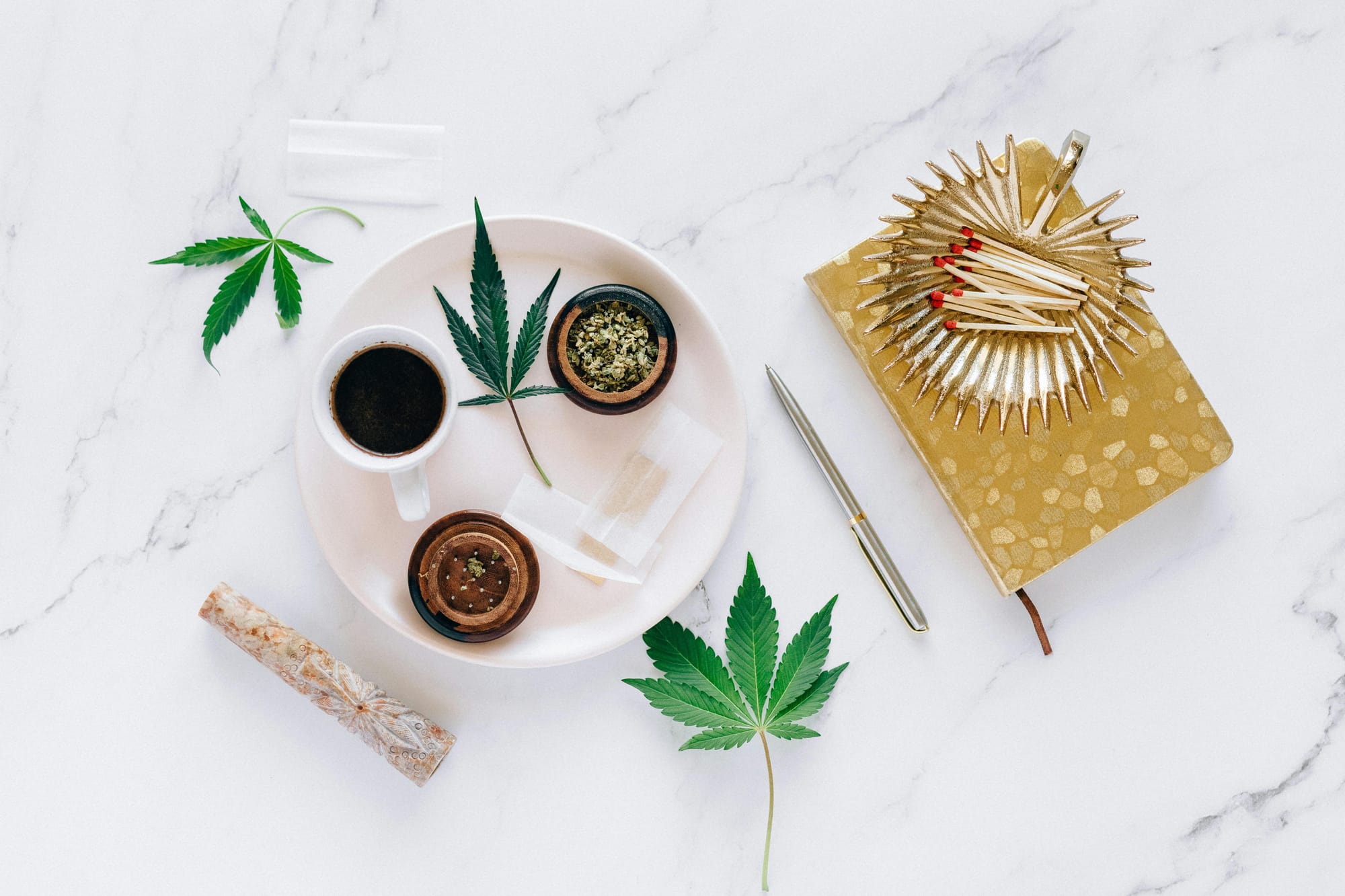
- CBD (Cannabidiol): Emerging as a promising alternative, CBD offers relief from inflammation and pain without the side effects associated with many prescription medications. With its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, CBD has been successfully used by individuals suffering from arthritis and post-joint replacement pain. Read about the benefits of CBD for arthritis pain and how it may enhance recovery and overall wellness.
How Do Joint Pain Relievers Work?
Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a key factor in joint pain. When joints become inflamed, the increased blood flow and fluid accumulation can lead to swelling, stiffness, and pain. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and meloxicam, work by inhibiting enzymes that promote inflammation. Topical agents like Voltaren gel deliver diclofenac—a potent anti-inflammatory—to the site of pain, reducing both inflammation and discomfort.
Blocking Pain Signals
Acetaminophen and opioids work primarily by altering the way the brain processes pain signals. Acetaminophen is believed to affect certain chemicals in the brain, which results in a decreased perception of pain. Opioids, while effective at reducing pain, carry a high risk of addiction and other serious side effects, making them less desirable for long-term management.
Modulating the Nervous System
Chiropractic care and acupuncture tap into the body’s natural healing mechanisms by addressing issues within the nervous system. For instance, acupuncture is thought to stimulate specific neurons that trigger an anti-inflammatory response. Studies have found that when applied correctly, acupuncture can activate the vagal-adrenal axis—a pathway that plays a critical role in controlling inflammation. This acupuncture research illustrates how traditional practices are supported by modern science.
Enhancing Recovery Through Alternative Approaches
Complementary therapies like CBD and cupping not only target pain but also promote overall healing. CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system can lead to reduced inflammation, improved sleep, and decreased anxiety—all factors that contribute to better pain management. Similarly, cupping therapy enhances local blood circulation, which can accelerate the body’s natural repair processes.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Joint Pain
Joint pain is not a one-size-fits-all condition; its treatment often depends on the location and underlying cause.
Knee Pain
Knee pain is particularly common, especially among older adults and those with a history of joint injury. Conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tears, or osteoarthritis can cause discomfort when bending the knee. Non-surgical interventions include physical therapy, the use of knee braces, and targeted exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the joint. For those suffering from knee pain when bending, resources like this knee pain relief guide offer practical advice on managing and alleviating symptoms.
Back and Neck Pain
Chronic back and neck pain can be debilitating and may require a multifaceted treatment approach. Many patients find that a combination of physical therapy, topical treatments (like lidocaine patches), and even alternative therapies such as acupuncture provide the best relief. Studies have indicated that topical lidocaine can be effective in reducing pain intensity in certain populations. Additionally, non-invasive methods like cupping therapy and chiropractic adjustments have shown promise in easing back pain without the need for surgery. For more on non-surgical treatments for back pain, consider exploring chronic back pain treatments.
Hand and Finger Pain
Joint pain in the hands, particularly in the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, can greatly impair daily tasks such as gripping and writing. Treatments for MCP joint pain may include activity modification, splinting, and the use of anti-inflammatory medications. In some cases, minimally invasive procedures or targeted physiotherapy may be recommended. For those interested in specialized approaches to hand pain, a useful resource is this MCP joint pain relief guide.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Each treatment modality has its own set of benefits and potential drawbacks:
- NSAIDs and Acetaminophen:
– Pros: Widely available, effective for mild to moderate pain, and relatively inexpensive.
– Cons: Long-term use may lead to gastrointestinal issues or liver damage, and NSAIDs may not be suitable for people with certain heart or kidney conditions. - Topical Treatments:
– Pros: Targeted pain relief with fewer systemic side effects, easy to apply.
– Cons: May not be effective for deep joint pain or widespread pain conditions. - Chiropractic and Acupuncture:
– Pros: Non-invasive, holistic approach that addresses underlying issues beyond just pain symptoms.
– Cons: Results can vary between individuals, and finding a qualified practitioner is essential for effective treatment. - Alternative Therapies (CBD, Cupping):
– Pros: Offer natural pain relief with minimal side effects, can complement other treatments.
– Cons: Research is still evolving, and product quality may vary—making it important to choose reputable sources. For example, CBD for arthritis pain has shown promise, but quality and dosing are key. - Opioids:
– Pros: Highly effective for severe pain in the short term.
– Cons: High risk of dependency, tolerance, and a range of side effects that make them unsuitable for long-term use.
Integrating Treatments for Optimal Results
For many individuals, the most effective approach to joint pain management is a multimodal one—combining several treatments to address different aspects of pain. For example, a treatment plan might include the use of NSAIDs for general pain relief, supplemented by physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve joint stability, and enhanced by alternative treatments like acupuncture or CBD to reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being.
This integrated approach not only alleviates pain but also supports long-term joint health. Emphasizing patient education is vital, as understanding how different treatments work together can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition.
Practical Tips for Managing Joint Pain
Managing joint pain is not only about choosing the right treatment—it’s also about lifestyle modifications that support overall joint health. Here are some practical tips:
- Stay Active: Regular low-impact exercise helps maintain joint mobility and strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts extra stress on weight-bearing joints, particularly the knees and hips.
- Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber can reduce systemic inflammation.
- Use Assistive Devices: Braces, orthotics, or specialized footwear can help alleviate stress on painful joints.
- Prioritize Rest and Recovery: Ensure adequate sleep and take breaks from repetitive activities to allow your joints to recover.
- Explore Complementary Therapies: Consider adding alternative treatments like acupuncture, cupping, or CBD into your regimen to enhance pain relief and overall wellness.
Conclusion
For anyone navigating the challenges of joint pain, it is encouraging to know that safe and effective alternatives exist. Whether you choose traditional pharmacologic options like NSAIDs or explore innovative alternatives that target inflammation and promote natural healing, the goal remains the same: to enhance mobility, improve quality of life, and foster long-term joint health.
By combining knowledge, practical tips, and the latest research insights, this exploration of joint pain relievers aims to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. With the right combination of therapies, tailored to each unique situation, relief is not only possible it is within reach.
Ultimately, the best treatment is one that addresses not just the symptoms but also the underlying factors contributing to joint pain. By taking a proactive, informed, and personalized approach, managing joint pain can transform from a constant struggle into a manageable, even conquerable, aspect of life.
Sources: